About me Hypnotherapy Issues Fees Supervision Blog Contact. Mednick.
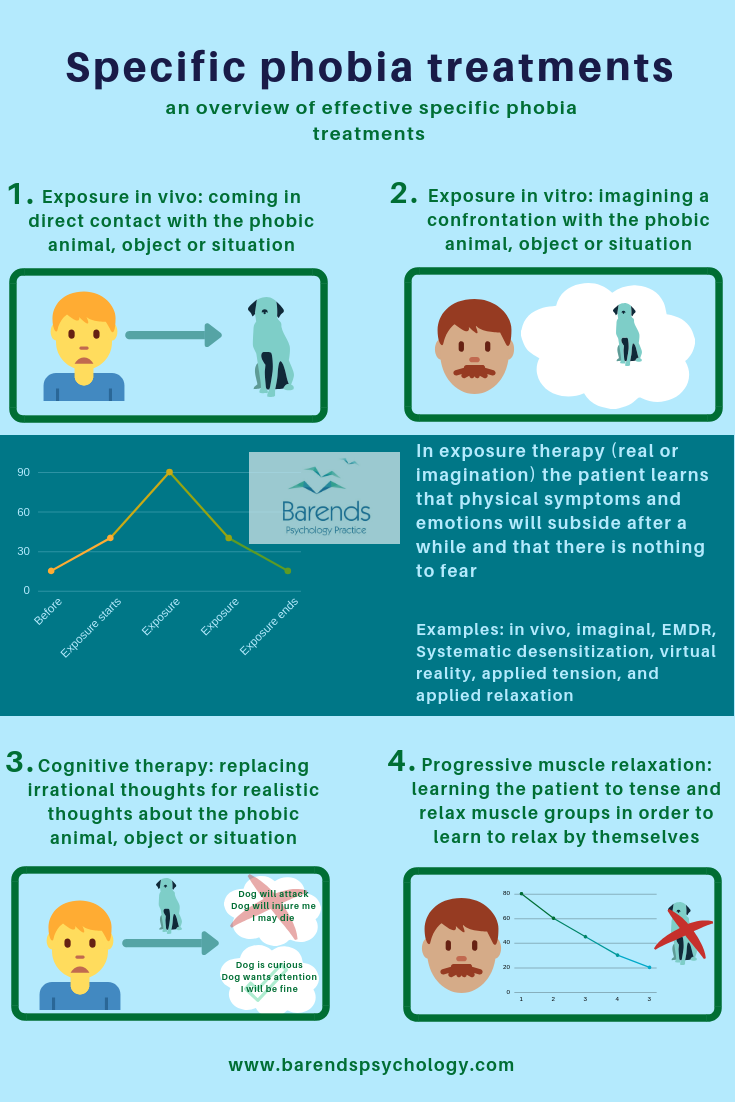
Phobia Treatment What Are The Most Effective Specific Phobia Treatments
Notes for Psychotherapists who want to work with needle phobic patients.
. A specific behavioral method for treatment of blood phobia Behav Res Ther. Definitions typesexamples case studies of phobias Types. The technique involves tensing the muscles in your body which then raises your blood pressure.
In fact textbooks seem to suggest that it is the major if not exclusive behavioral intervention for BII phobia eg Barlow Durand 2005. Since this method is as effective as the other treatments in only half the time applied tension should clinically be the treatment of choice for blood phobia. It is specifically useful for phobias associated with fainting usually needle and blood therapies.
Ost Sterner 1987. Most psychotherapists are simply unprepared for a patient to become unresponsive and possibly begin convulsing. Holly Torbit.
This reaction can be and often is precipitated by simply talking about or having the patient imagine a needle procedure. Psychotherapists and Needle Phobia. Applied tension to help prevent fainting related to phobias Bristol Hypnotherapy.
When doing applied tension you cross your legs clasp your hands in front of your chest and pull as hard as you can tensing all the big muscles of your body abs glutes thighs etc. Blood-injury-injection BII type phobias often come with a vasovagal ie fainting response that results from a sudden drop in blood pressure ie vasovagal syncope. What is unknown is whether an individual can overcome blood phobia through self-arranged.
However surprisingly little empirical evidence is available on the additive. Thirty patients with phobia for blood wounds and injuries were treated individually with applied tension applied relaxation or the combination of these two methods for 5 9 and 10. Vasovagal syncope is a common clinical problem that is often difficult and expensive to diagnose and treat.
Thirty patients with phobia for blood wounds and injuries were treated individually with applied tension AT exposure in vivo E or tension-only T for 5 sessions. A case meeting DSM-IV criteria for specific phobia blood-injection-injury type illustrates that cognitive factors may prevent full compliance with applied tension and that behavioural experimentation is a useful strategy for dealing with such phenomena. Explanations of phobias Behavioural classical.
AB - Vasovagal syncope is a common clinical problem that is often difficult and expensive to diagnose and treat. Despite a failure to find between-group differences on many measures there was a trend favoring applied tension. The current recommended treatment for BII phobia is Applied Tension AT a tension technique that includes in vivo exposure.
The good news is that applied tension is a highly effective technique you can use with your patients who suffer from blood or injection phobias. The results in our previous blood phobia study 0st et al 1991 showed that applied tension and tension-only were better than exposure in vivo. This study examined the effects of applied muscle tension a respiratory intervention and a no treatment control condition on presyncopal symptoms and cerebral oxygenation during a simulated.
1 The Applied Tension Technique was developed by Lars-Göran Öst. Thus muscle tension techniques seem to be well suited as the primary intervention tool for behavioral BII-phobia treatment. The technique involves tensing the muscles in your body which then raises your blood pressure.
Fear of blood and needles increases risk for presyncopal symptoms. Applied tension to help prevent fainting related to phobias. The Applied Tension Technique1 is a strategy developed to help prevent fainting or help people recover faster if they do faint.
The conclusion from this is that the tension technique is the most important part in the applied tension treatment. For blood phobia the expert typically first helps the client learn applied muscle tension to prevent fainting and then stages the exposure trials Ayala Meuret. However it is not universally effective.
Where people have other anxieties they may obtain more general benefit from the exposure part of the treatment on standard fear surveys as the tension coping skill only really benefits blood-injection-injury type phobias although it does appear to do so regardless of whether fainting is a problem Ayala at al 2009. Applied tension or tension-only should from a clinical point of view be considered the treatment of choice for blood phobia. You can do this sitting up or lying down I would.
Applied tension for BII phobia the final answer. Applied muscle tension can prevent or attenuate presyncopal symptoms. Applied tension is a behavioral technique that.
Agoraphobia blood phobia dog phobia. Applied Tension for BII Phobias. Up to 24 cash back The Applied Tension Technique is a strategy developed to help prevent fainting or help people recover faster if they do faint.
Applied tension AT is one strategy that can be used to counteract this visceral response. Blood-injury-injection BII phobia presents with a unique anxiety response that often involves blood pressure drops and pronounced bradycardia which can culminate in fainting. Chapman.
Applied tension is an effective and relatively inexpensive treatment for patients with vasovagal syncope related to injection phobia and may hold promise as a treatment for other types of syncope. More than half of people with needle phobias and almost three-quarters of people with blood phobias have fainted when they are faced with their feared. Applied tension is an effective and relatively inexpensive treatment for patients with vasovagal syncope related to injection phobia and may hold promise as a treatment for other types of syncope.
If your blood pressure increases you are less likely to faint. Applied tension should clinically be the treatment of choice for blood phobia because it is as effective as the other treatments in only half the time and there was a trend favoring applied tension. Applied tension or tension-only should from a clinical point of view be considered the.
AT differed significantly and T marginally from E at both assessments. Sion tension-only exposure-only applied relaxation used to treat BII phobia has found incon- clusive evidence for which component of treatment is most effective in addressing patient fear reactions and fainting symptoms Ayala Meuret Ritz 2009. Thirty patients with phobia for blood wounds and injuries were treated individually with applied tension applied relaxation or the combination of t.

Phobias Persistent Irrational Fear Of Specific Object Which Leads To Avoidance And Interference In Daily Life Ppt Download

0 Comments